Geometric Constraints - relationships between sketch entities.
All entities have to be constrained - their position and characteristics described and formalised. This can be achieved through Dimensional or Geometric constraints. Dimensional constraints show a linear or angular distance between entities. Geometric constraints are more fundamental than this and describe the characteristics of the relative position of entities.
Always sort out your Geometric Constraints before your Dimensional Constraints. They are more robust and better capture your design intent.
The Sketcher Intent Manager will automatically assign Geometric constraints as you sketch - do not allows constraint to be assigned if they go against your design intent. As with dimensions, geometric constraints can be selected and deleted
Sometimes selection can be a bit tricky, if you cannot highlight a constraint by hovering your mouse over it then whilst in the correct position either;
- Right Click menu [press and hold RMB] > pick from list - this will show all entities under the mouse pointer.
- or, toggle through all the entities in that list with a momentary/quick RMB click until the one you want highlights then LMB to select.
![]()
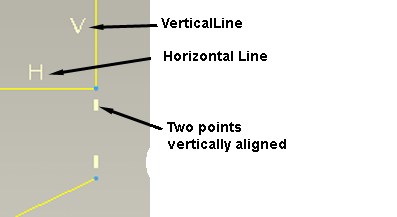
Vertical - a line aligned vertically or two points vertically aligned
![]()
Horizontal - a line aligned horizontally or two points horizontally aligned
![]()
Perpendicular - 2 curves at 90 degrees to each other - this could be line/line, arc/line, arc/arc
![]()
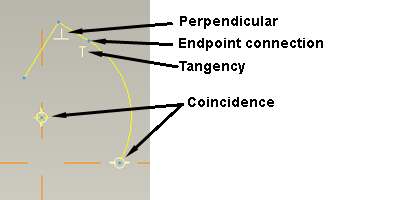
Tangency - at the point they meet, two entity are travelling in the same direction - line/arc or arc/arc. Effectively a smooth transition between two entities.
![]()
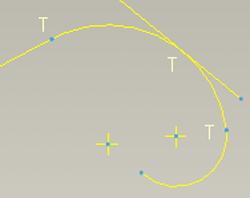
Midpoint - constrains a point to always be half way along a line
![]()
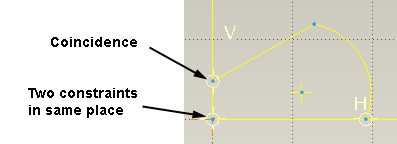
Coincidence - puts two entities in the same place. Two points, a point on a line, two lines, two arc centre points [concentricity]. Watch closely for two coincidence constraints in the same place, notice the horizontal and vertical white bars around the constraint circle.
![]()
Symmetry Centreline - using a centreline as a construction line, you can constrain two points, commonly curve/line endpoints to remain equally spaced each side of that centreline.
![]()
Equality - make two entities equal - lines equal length, arcs equal radius.
![]()
Parallelism - make two lines parallel
![]()